Swate QuickStart
last updated at 2024-04-18DataPLANT provides the tool Swate to support you in data annotation. In this guide, we focus on adding metadata to your studies and assays with our tool. Use the isa.study.xlsx to describe the characteristics of your samples, e.g. how you grew your plant, and isa.assay.xlsx to annotate the experimental analyses.
UserNewbie ModeTutorial💡 Consider reading about Swate
💡 We assume that you already created an ARC that contains one or more isa.study.xlsx and isa.assay.xlsx file(s), respectively.
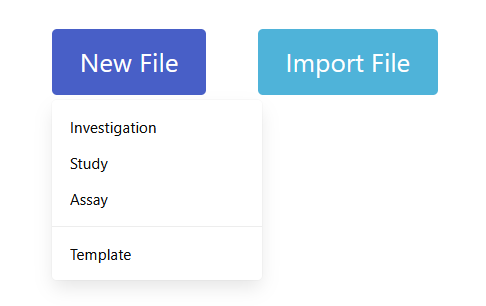
- To create an annotation table with the Swate standalone in your browser, click "New File" and select which kind of annotation table you want to create. If you already created a isa.study.xlsx or isa.assay.xlsx file, you can select "Import File" to modify and add to it.
- To create an annotation table within ARCitect, add a new table to your assay or study by clicking the plus (+) symbol next to your metadata sheet
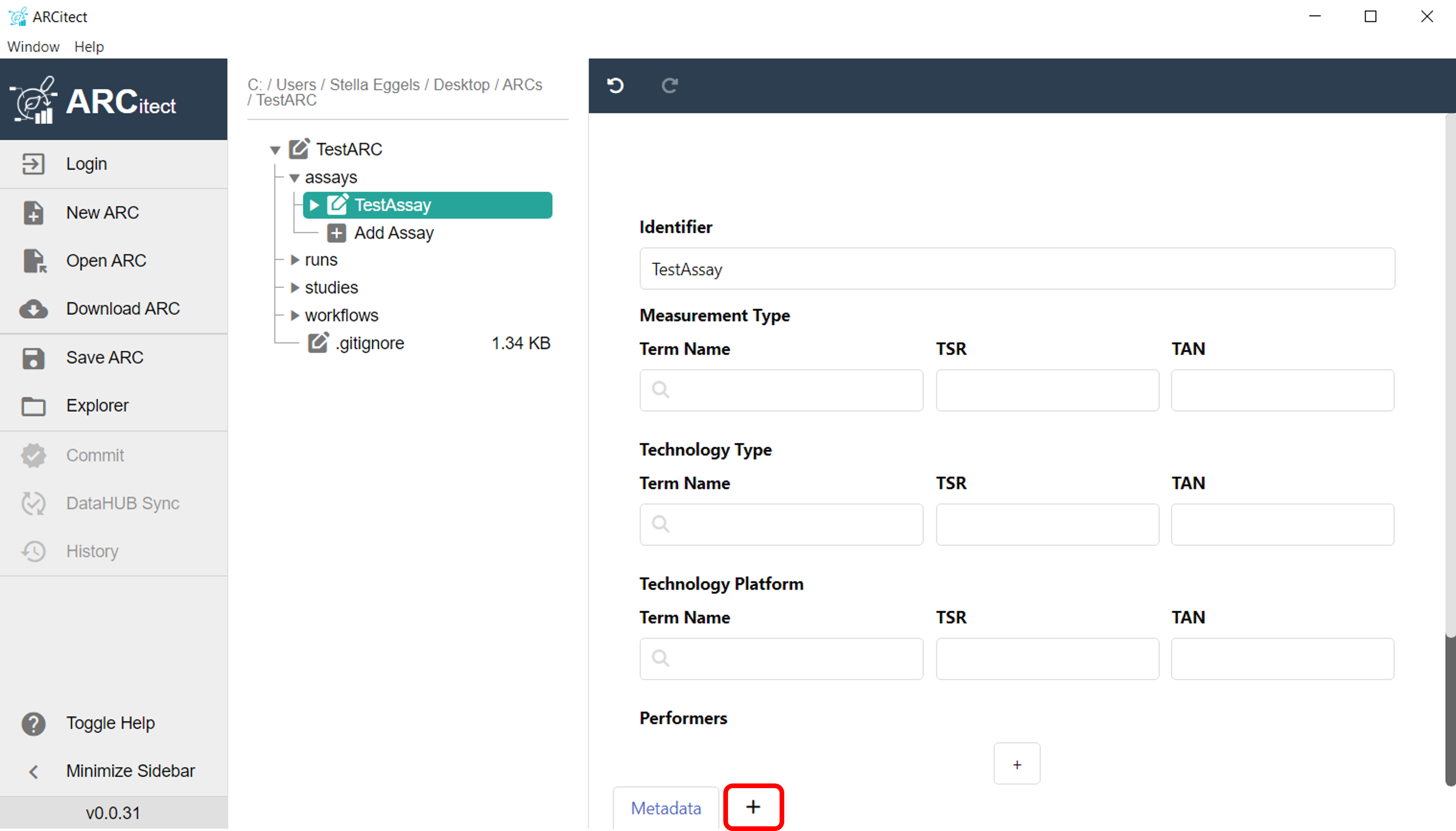
Fill in the metadata sheet of your study or assay
Create and fill your annotation table with help of the annotation principles.
Briefly:- Characteristics are used for study descriptions and describe inherent properties of the source material (e.g. a certain strain)
- Parameters describe steps in your experimental workflow (e.g. a measurement temperature)
- Components describe physical obsjects of your protocol (e.g. an instrument name)
- Factors describe independent variables that result in a specific output (e.g. the light intensity)
The combination of ISA terms (Characteristics, Parameter, Component, Factor) and biological or technological ontology terms (e.g. temperature, strain, instrument model) gives the flexibility to display an ontology term, e.g. temperature, as a regular process parameter or as the factor your study is based on (Parameter [temperature] or Factor [temperature]).
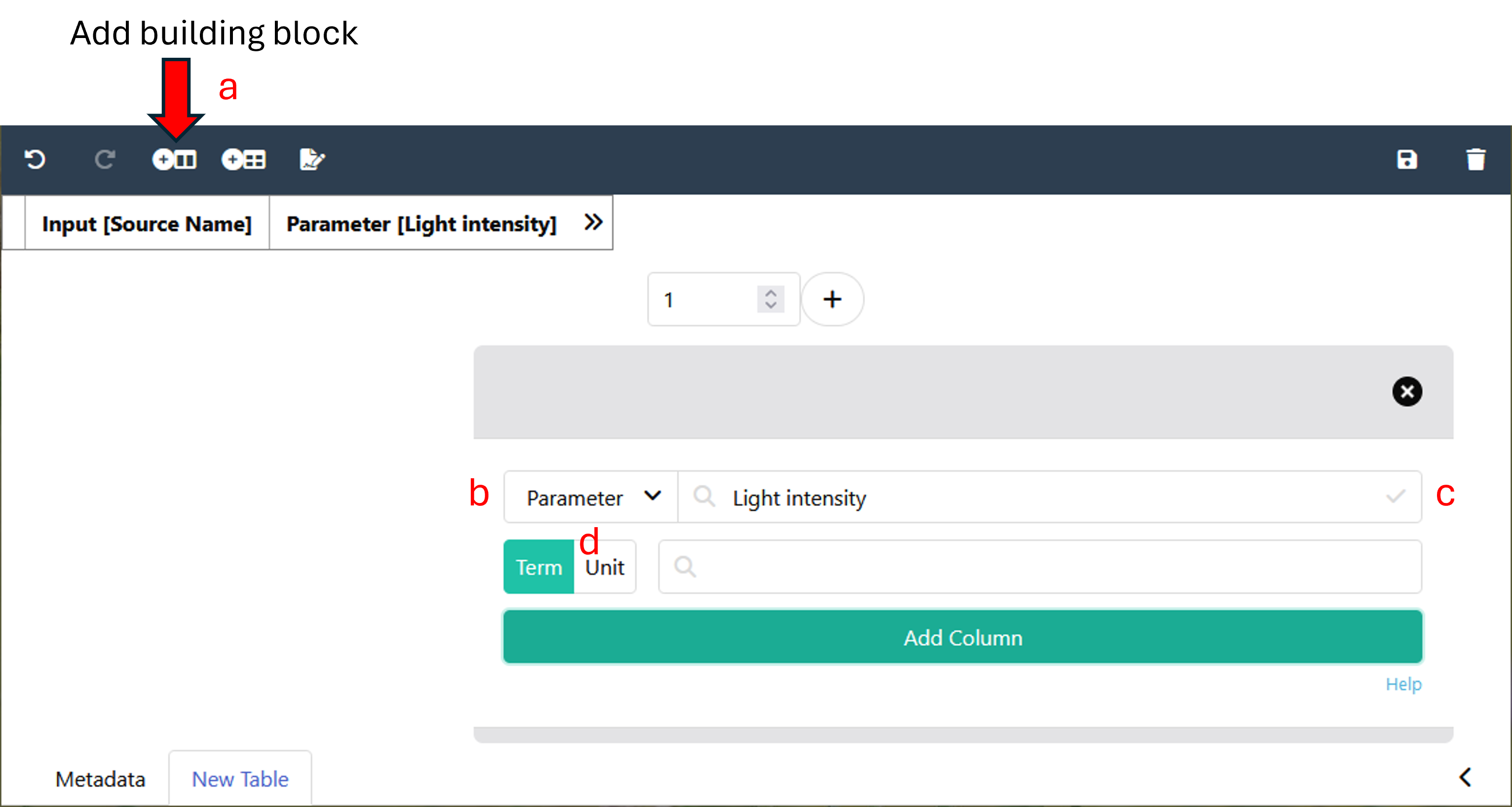
To add a building block, click the "add building block" symbol ( a ) in the top left corner.
Choose the type of building block you want to add ( b ).
If you chose a descriptive building block type (building blocks besides Input and Output), use search field ( c ) to search for an ontology term. Swate accesses the SwateDB with a list of established external ontologies designated suitable for use in plant science. In addition, we feature our own ontology DPBO to extend the DB with missing, but necessary terms.
If you want to add a building block with a unit, activate the unit box ( d ) and use the search field to look for a fitting unit term, e.g. degree Celsius as unit for Parameter [temperature].
- For more information on customizing your annotation table click here.
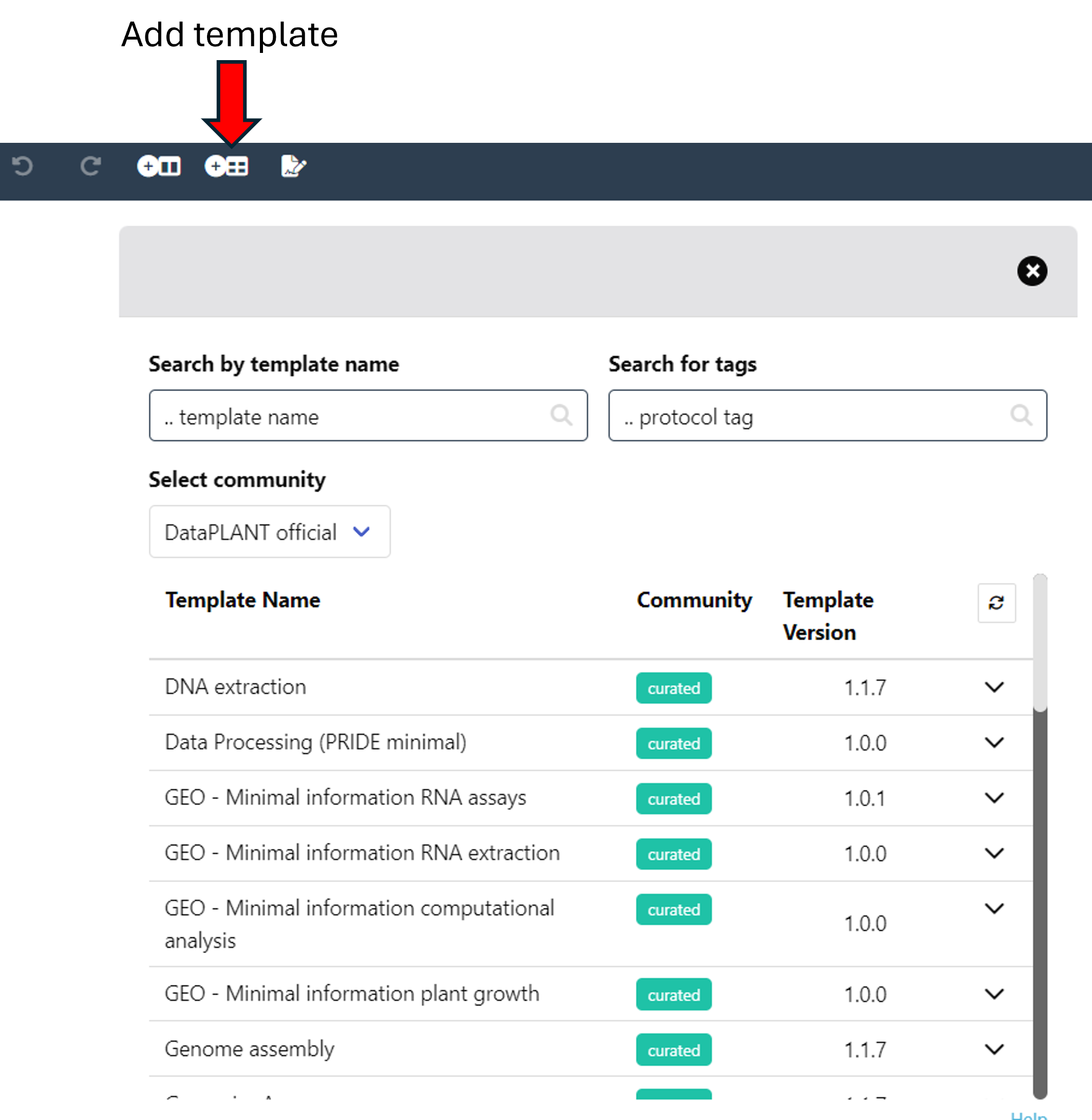
Alternatively, you can also use one of DataPLANT’s Swate templates. You can find them via the "add template" button, next to the "add building block" button.
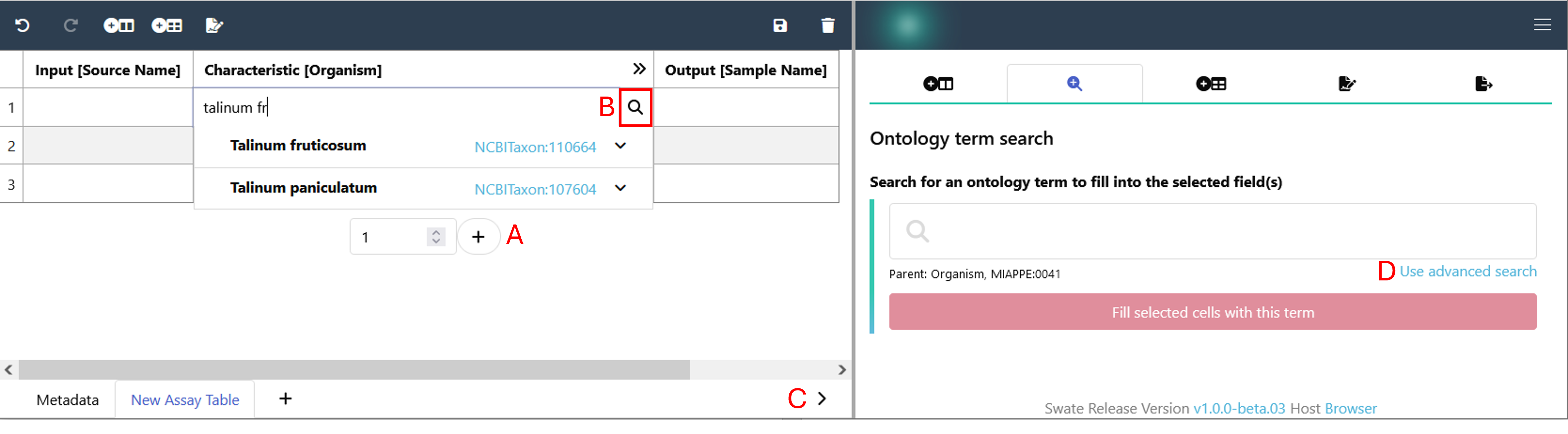
Add rows beneath the building blocks with the plus symbol ( A ) and fill the cells with ontology terms to note the respective Characteristics, Parameter, Component and Factor values of your experiment. By activating the ontology term search function (magnifying glass, B), you can fill cells with ontology terms.
When Ontology term search ( B ) is enabled, Swate will suggest a selection of suitable terms from the ontology database for the column header, e.g. TripleTOF 5600 for instrument model. Alternatively to activating the Ontology term search within the cells of your annotation table, you can use the ontology term search panel on the right side after expanding it with the arrow on the bottom right ( C ).
If you could not find a fitting term, you can use the advanced term search with the blue link ("use advanced search", D) below the ontology term search field in the right panel.
If you still could not find a fitting term, use free text input.
Note: More information on how to use Swate can be found here.