Home
Fundamentals
Research Data Management
FAIR Data Principles
Metadata
Ontologies
Data Sharing
Data Publications
Data Management Plan
Version Control & Git
Public Data Repositories
Persistent Identifiers
Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN)
DataPLANT Implementations
Annotated Research Context
User Journey
ARC specification
ARC Commander
QuickStart
QuickStart (Experts)
Swate
QuickStart
Walk-through
Best Practices For Data Annotation
DataHUB
DataPLAN
Ontology Service Landscape
ARC Commander Manual
Setup
Git Installation
ARC Commander Installation
Windows
MacOS
Linux
ARC Commander DataHUB Access
Before we start
Central Functions
Initialize
Clone
Connect
Synchronize
Configure
Branch
ISA Metadata Functions
ISA Metadata
Investigation
Study
Assay
Update
Export
ARCitect Manual
Installation - Windows
Installation - macOS
Installation - Linux
QuickStart
QuickStart - Videos
ARCmanager Manual
What is the ARCmanager?
How to use the ARCmanager
Swate Manual
Swate Installation
Excel Browser
Excel Desktop
Windows – installer
Windows – manually
macOS – manually
Organization-wide
Core Features
Annotation tables
Building blocks
Building Block Types
Adding a Building Block
Using Units with Building Blocks
Filling cells with ontology terms
Advanced Term Search
Templates
File Picker
Expert Features
Contribute Templates
ISA-JSON
DataHUB Manual
Overview
User Settings
Generate a Personal Access Token (PAT)
Projects Panel
ARC Panel
Forks
Working with files
ARC Settings
ARC Wiki
Groups Panel
Create a new user group
Data publications
Passing Continuous Quality Control
Submitting ARCs with ARChigator
Track publication status
Use your DOIs
Guides
ARC User Journey
Create your ARC
ARC Commander QuickStart
ARC Commander QuickStart (Experts)
ARCitect QuickStart
Annotate Data in your ARC
Annotation Principles
ISA File Types
Best Practices For Data Annotation
Swate QuickStart
Swate Walk-through
Share your ARC
Register at the DataHUB
DataPLANT account
Invite collaborators to your ARC
Sharing ARCs via the DataHUB
Work with your ARC
Using ARCs with Galaxy
Computational Workflows
CWL Introduction
CWL runner installation
CWL Examples
CWL Metadata
Recommended ARC practices
Syncing recommendation
Keep files from syncing to the DataHUB
Working with large data files
Adding external data to the ARC
ARCs in Enabling Platforms
Publication to ARC
Troubleshooting
Git Troubleshooting
Contribute
Swate Templates
Knowledge Base
Teaching Materials
Events 2023
Nov: CEPLAS PhD Module
Oct: CSCS CEPLAS Start Your ARC
Sept: MibiNet CEPLAS Start Your ARC
July: RPTU Summer School on RDM
July: Data Steward Circle
May: CEPLAS Start Your ARC Series
Start Your ARC Series - Videos
Events 2024
CEPLAS ARC Trainings – Spring 2024
MibiNet CEPLAS DataPLANT Tool-Workshops
Frequently Asked Questions
last updated at 2024-01-18
What is CWL?
CWL is short for Common Workflow Language.
It is an open standard for describing how to run command line tools and connect them to create
workflows, which can then be incorporated in other workflows if needed (nested workflows).
Descriptions in CWL are portable across a variety of platforms that support the CWL
standards. It enables scaling of complex workflows from single user workstations to hpc environments.
The goals of CWL align with the FAIR principles:

Processing objects in CWL
CWL consists of four different possible processing objects: Command-Line Tools, Expression Tools, Workflows and Operations.
Each of the first three processing objects can be executed individually using a cwl-runner or be part of a larger workflow.
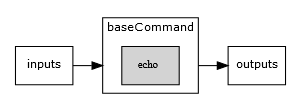
Command-Line Tool
This processing object is a wrapper for command like arguments, such as ls, echo or compiled
command line tools. The executed command is defined in the baseCommand attribute. It's basic structure
consists of a base command, inputs and outputs.
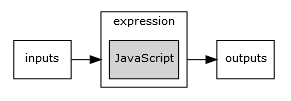
Expression Tool
This process executes a pure JavaScript expression. It is used for complex expressions during workflows
that operate on the input data and produce an output. It's basic structure consists of an JavaScript expression,
inputs and outputs.
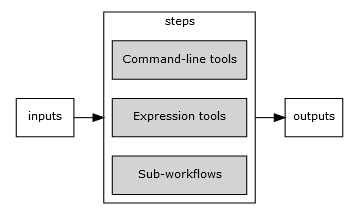
Workflows
A workflow is a processing object that can execute command-line tools, expressions tools, or workflows as steps.
The step processing units can be present in any configuration. It's basic structure consists of steps, inputs and outputs.
Operation
This processing object is intended as a placeholder during development or for visualization. It does not contain enough
information to be executed. It consists of inputs and outputs.
Useful Links
Image Sources



