Working together
Options to share an ARC via the DataHUB
Section titled “Options to share an ARC via the DataHUB”To suit a wide range of collaborative scenarios, the DataHUB offers multiple, flexible ways of sharing an ARC. This flexibility can be confusing at first. Generally, ARCs can be uploaded to the DataHUB and (a) associated to the namespace of a user account (the default) or (b) the namespace of a group.
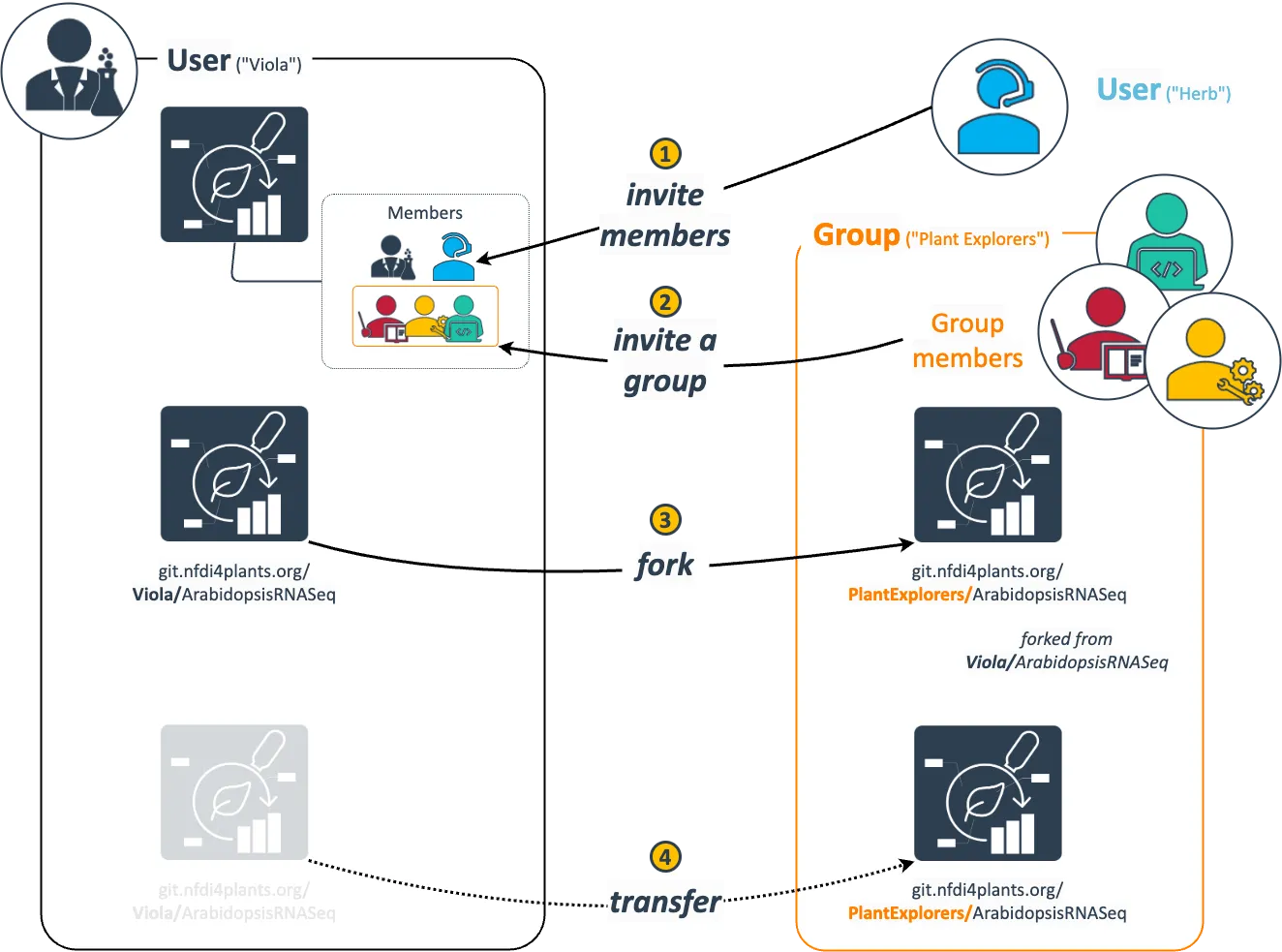
The figure below is supposed to give a quick overview. Once an ARC exists in the DataHUB, you can choose between these options to share the ARC with collaborators.
- You can invite individual users (1). This is helpful to share an ARC with selected colleagues.
- To share an ARC with a group of users (e.g. a lab or consortium), you can invite a group (2).
In both cases (1 and 2), the ARC “stays associated” with the original owner only (visible by the namespace and URL address). Furthermore the roles and permissions can be set for individual users and groups.
-
Alternatively, you can create a fork of your ARC (3). This generates a copy linked to the original ARC, but now associated with the group. This can be used to share an ARC at a certain stage, without sharing the full progress after that stage. However, since the two ARCs (the original and the fork) can now be developed independently. This can easily lead to divergence and requires a bit more technical expertise to keep both ARCs in sync (if desired).
-
Finally, you can transfer your ARC to a group (4). This moves the ARC to new namespace (that of the group).
In both cases 3 and 4, you must have at least maintainer access to the group. If you have maintainer access, you can also directly create or upload an ARC to a group.
The visibility of ARCs and groups can be managed individually for each ARC (see ARC settings) or group see (Creating a Group).
- Private – Access must be granted explicitly to each user or a group.
- Internal – Can be accessed by any logged in user.
- Public – Can be accessed without authentication.
Roles and permissions
Section titled “Roles and permissions”If you create or upload an ARC to the DataHUB, you are the Owner by default. When inviting new members to an ARC or group, you can choose between different roles.
- Guest – Has the least rights. They will not be able to see the content of an ARC (only the wiki page).
- Planner – Has access to issues and project planning features (like boards and milestones) without access to the content of an ARC.
- Reporter – Has read access to your ARC. This is recommended for people you ask for consultancy.
- Developer – The choice for most people you want to invite to your ARC. Developers have read and write access, but cannot maintain the project on the DataHUB, e.g. invite new members.
- Maintainer – Has read and write access and can add or remove members, except for yourself. This is the minimum role recommended for inviting group leaders as it allows them to add their group members for data upload or analysis to the project.
- Owner – An owner has basically all rights to the ARC. They can delete or transfer the ARC and manage user memberships.
In the DataHUB, namespaces help organize related projects.
- Every user has a personal namespace, where they can upload or create new ARCs.
- Every group and subgroup has an own namespace, respectively.
You can check the namespace by looking at the URL. For example:
| Type | URL | Namespace | Display Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| A personal ARC | https://git.nfdi4plants.org/brilator/Facultative-CAM-in-Talinum | brilator | Dominik Brilhaus |
| A group-shared ARC | https://git.nfdi4plants.org/ceplas/triesch2023_brassicaceae_transposons | ceplas | CEPLAS |