CWL Runner Installation
The recommended CWL runner is cwltool, the reference implementation for the CWL standards.
The installation on Windows can be done following the guide here.
-
Install Windows Subsystem for Linux from the Microsoft Store
-
Install Debian from the Microsoft Store
-
Set Debian as your default WSL 2 distro:
- Open Windows PowerShell
- Type
wsl --set-default debianand hit enter
-
Install Docker Desktop for Windows
- Start Docker Desktop and Navigate to Settings
- Select “Use WSL 2 based engine” in the general tab and apply
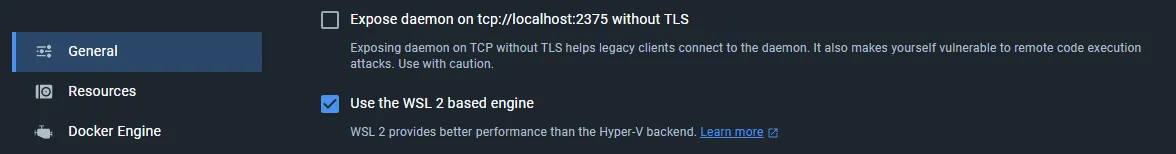
- Select “Enable Integration with my default distro” in the resources tab under WSL Integration

-
Start WSL:
- Open Windows PowerShell
- Type
wsland hit enter - You may need to specify a username and password if this is your first time using WSL (the password doesn’t show when typing, just type and hit enter)
-
Follow the Instructions for Linux (Debian/Ubuntu) in this tutorial
For installation on Linux (Debian/Ubuntu):
- Run
sudo apt-get updatein the console - Install Python 3 if it is not already installed by executing the command
sudo apt install python3 - Install python virtual environment with
sudo apt install python3.11-venv- You may need to change the version of python, depending on your installation
- You can check the installed version with
python3 --version
- Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv env- The environment is named env here, the name can vary
- Activate the virtual environment with
source env/bin/activate- If you want to activate the environment from a different location, you must enter the full path to the installation location
- e.g. if you installed it in your home directory, you would use
source /home/username/env/bin/activate
- e.g. if you installed it in your home directory, you would use
- If you want to activate the environment from a different location, you must enter the full path to the installation location
- Install the cwltool with pip by running
pip install cwltool
- Install conda-forge
- Install cwltool via
conda install -c conda-forge cwltool
- If you are on Windows, start the WSL
- Activate the virtual environment
source env/bin/activate- If you want to activate the environment from a different location, you must enter the full path to the installation location
- e.g. if you installed it in your home directory, you would use
source /home/username/env/bin/activate
- e.g. if you installed it in your home directory, you would use
- If you want to activate the environment from a different location, you must enter the full path to the installation location
- Run
cwltoolby specifying the CWLWorkfloworCommandLineTooldescription file path and the (optional) inputs file path (you can use relative or full paths):
cwltool path/to/cwlfile.cwl path/to/jobfile.yml- If you are in an ARC, you can navigate to the runs folder and type
wslin the address line to start the WSL at that location and execute a typical run after activating the virtual environment (see second step) with the command:
cwltool ./myRun/run.cwl ./myRun/run.yml- CWL copies the relevant files to temporary directories located on the disc where your WSL is installed. If you want them on a different disk for perfomrance/size reasons, you can use the
--tmpdir-prefixand--tmp-outdir-prefixoptions to specify the location of the temporary directories:
cwltool --tmp-outdir-prefix=/mnt/c/Users/myUser/Tempdir/ --tmpdir-prefix=/mnt/c/Users/myUser/Tempdir/ ./myRun/run.cwl ./myRun/run.ymlHere is a very simplified example to check, that your cwltool installation functions
-
Store the following as
echo-tool.cwl#!/usr/bin/env cwl-runnercwlVersion: v1.2class: CommandLineToolbaseCommand: [echo]stdout: message.txtinputs:message:type: stringinputBinding:position: 1outputs:output:type: stdout -
In the same folder, store the following as
job.ymlmessage: "I love ARCs and CWL" -
Now you can execute the tool
- providing an
inputdirectly via CLI:
cwltool echo-tool.cwl --message "ARCs are great"or
- providing the
inputvia thejob.yml:
cwltool echo-tool.cwl job.yml - providing an
-
Both create an
outputfile calledmessage.txtwith your specified message.