CWL Introduction
CWL is short for Common Workflow Language. It is an open standard for describing how to run command line tools and connect them to create workflows, which can then be incorporated in other workflows if needed (nested workflows). Descriptions in CWL are portable across a variety of platforms that support the CWL standards. It enables scaling of complex workflows from single user workstations to hpc environments.
The goals of CWL align with the FAIR principles:

Processing objects in CWL
Section titled “Processing objects in CWL”CWL consists of four different possible processing objects: Command-Line Tools, Expression Tools, Workflows and Operations. Each of the first three processing objects can be executed individually using a cwl-runner or be part of a larger workflow.
Command-Line Tool
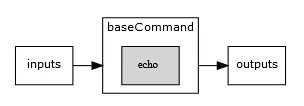
Section titled “Command-Line Tool”This processing object is a wrapper for command like arguments, such as ls, echo or compiled
command line tools. The executed command is defined in the baseCommand attribute. It’s basic structure
consists of a base command, inputs and outputs.
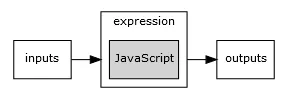
This process executes a pure JavaScript expression. It is used for complex expressions during workflows that operate on the input data and produce an output. It’s basic structure consists of an JavaScript expression, inputs and outputs.
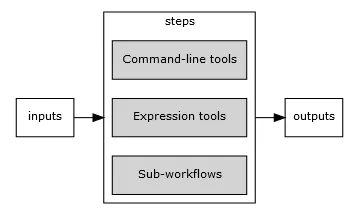
A workflow is a processing object that can execute command-line tools, expressions tools, or workflows as steps. The step processing units can be present in any configuration. It’s basic structure consists of steps, inputs and outputs.
This processing object is intended as a placeholder during development or for visualization. It does not contain enough information to be executed. It consists of inputs and outputs.